Meta-Reinforcement Learning for Spacecraft Proximity Operations Guidance and Control in Cislunar Space
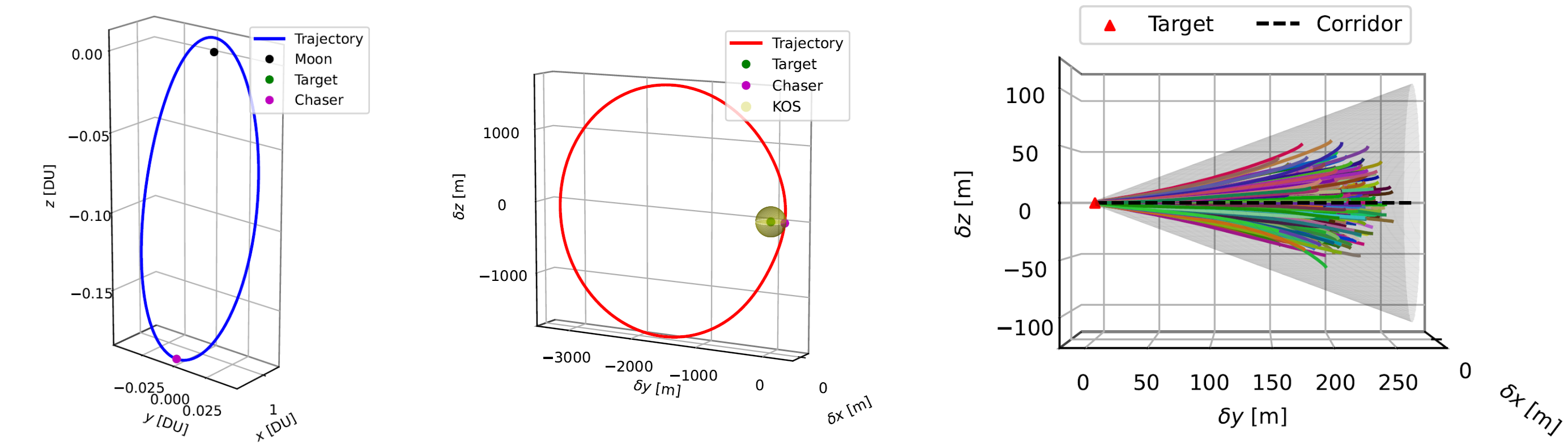
In order to address the challenges of future space exploration, new lightweight and model-free guidance algorithms are necessary to make the spacecraft completely autonomous. In recent years, autonomous spacecraft guidance has been a subject of intense research, and in the near future, this technology will be a great advantage for proximity operations in cislunar space. For instance, NASA’s Artemis program plans to establish a lunar Gateway, and this type of autonomous maneuver, besides the nominal Rendezvous and Docking (RVD) ones, is also necessary for the assembly and maintenance procedures. In this context, a Meta-Reinforcement Learning (Meta-RL) algorithm is applied to address the real-time relative optimal guidance problem of a spacecraft in the cislunar environment. Non-Keplerian orbits have more complex dynamics, and classic control theory may be less flexible and more computationally expensive with respect to Machine Learning (ML) methods. Furthermore, Meta-RL is chosen for its peculiar and promising ability of “learning how to learn” through experience. It is an ML approach in which a model is trained on a variety of tasks in such a way that it becomes more efficient and effective at learning new ones. A stochastic optimal control problem is modeled in the Circular Restricted Three-Body Problem (CRTBP) framework as a discrete time-scale Markov Decision Process (MDP). The agent, an LSTM-based network, is then trained with a state-of-the-art actor-critic algorithm known as Proximal Policy Optimization (PPO). Additionally, operational constraints and stochastic effects are considered to assess policy safety and robustness. An MLP-based agent and an optimal control solution using pseudospectral methods are also evaluated for comparison purposes. The resulting tool is a closed-loop controller able to autonomously guide a spacecraft in the context of cislunar proximity operations. It is able to approximate the optimal control solution with a very general and not hand-crafted algorithmic framework, guaranteeing at the same time high robustness and computational efficiency.
Read the MS Thesis Read the Presentation Read the Journal Paper
